A crucial component of the marketing process is the marketing funnel. It describes the simplest route that clients could follow to make a transaction. The marketing funnel is, in the end, a useful structure for communicating with and involving clients along their journey. Here, you’ll discover information about each level of the marketing funnel and how using Amazon Advertising in conjunction with full-funnel advertising may help marketers achieve their goals.
A marketing funnel is what?
Since more than a century ago, the idea of a marketing funnel has been used to categorise key moments in the purchasing process, from awareness to contemplation to choice to loyalty.
The customer journey, sometimes known as the conversion funnel, is related to it, but the path to buy nowadays is much more complicated, and very few customer journeys will perfectly match the funnel. A more thorough strategy, like full-funnel marketing, is used in successful marketing efforts to target customers at every stage of the buying cycle.
The form of the marketing funnel reflects the notion that during the first phases of a customer’s purchasing process, marketers cast a broad net to engage as many leads as they can before nurturing those leads through each step of the funnel. As you descend the funnel, the audience gets smaller, and at the bottom you have consumers who are most likely to convert and, hopefully, turn into devoted patrons.
The importance of marketing funnels
The idea is still crucial even though the customer journey may not be as straightforward as the one exemplified by the marketing funnel. The digital road to purchase is anything from linear, and the digital marketing funnel takes into consideration that customers join and exit the funnel and move across it, and that their buying isn’t restricted to a single business or location.
Given that customers may purchase whenever and wherever they choose, companies need to consider how to connect with them across the whole customer experience. Consumers may do comprehensive online research and product comparison at the consideration stage of the digital marketing funnel, which is no longer just restricted to in-store comparisons. Several businesses have adapted to this new method of purchasing and welcomed this less-linear path to purchase by establishing genuine and beneficial connections with clients at every stage of the funnel.
The lead generating and lead nurturing processes both benefit from the use of marketing funnels. Campaigns are used by businesses to draw in new leads throughout the awareness and consideration phases. Campaigns assist businesses expand existing leads and eventually turn customers into brand champions during the decision and loyalty stages. Connecting the links between what channels, methods, and content are generating the most attention, dialogues, and, eventually, sales for their business is made possible by digital marketing and the marketing funnel.
A marketing funnel’s stages
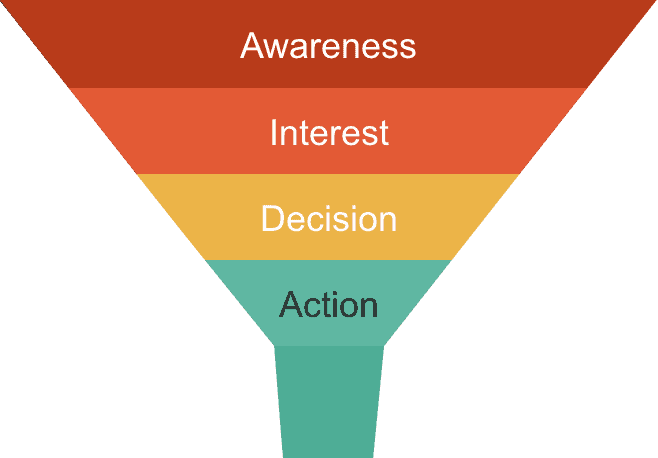
There is no one version of the funnel that is acknowledged worldwide, and several explanations include three, four, or five phases or more that customers take when buying. The stages of awareness, consideration, conversion, and loyalty are all included in the four-stage marketing funnel that will be described here.
Step 1: Awareness
Knowing a brand’s name, messaging, tone and style, values, and culture is referred to as having brand awareness. Brand awareness entails appealing people to a brand, as well as assisting them in recognising and remembering it. It starts with consumer research. By using pertinent client touch points along the road to buy, the aim is to keep the brand front of mind.
Step 2: consideration
Increasing the chance that shoppers will give a certain brand and its products some thought is the aim of consideration marketing. Consumers’ problems, interests, or questions should be addressed in marketing materials. Customers are currently attempting to learn more about a brand and determine what makes it unique from competing brands. Customers should be educated and informed by brands during the consideration process so they can see how your product or service will solve their problem.
Step 3: conversion
The conversion stage aims to persuade customers to buy a good or service because they think the brand they’ve chosen is the best one to address their issue or fulfil their requirement. This stage, which is also known as the “decision” or “buy” phase, gives brands the chance to invest in a plan that will help them stand out in their category and set themselves apart from competing goods. A well-thought-out product page on the website is crucial during this stage, as is providing outstanding customer care to help customers feel confident about their purchases.
Stage 4: Loyalty
By offering a smooth purchasing experience and a high-quality good or service, brands may encourage loyalty. Brands may continue to be top of mind for customers by maintaining contact and relationships after a sale.
Good interactions before, during, and after the buying process might affect whether a consumer becomes a repeat buyer. Without a strategy for increasing customer loyalty, businesses risk discovering that many consumers only make one transaction before leaving. Some marketers sometimes refer to this stage as the “engagement” stage since, on average, it costs a firm five times more to attract new customers than to keep ones they already have.





There are no comments